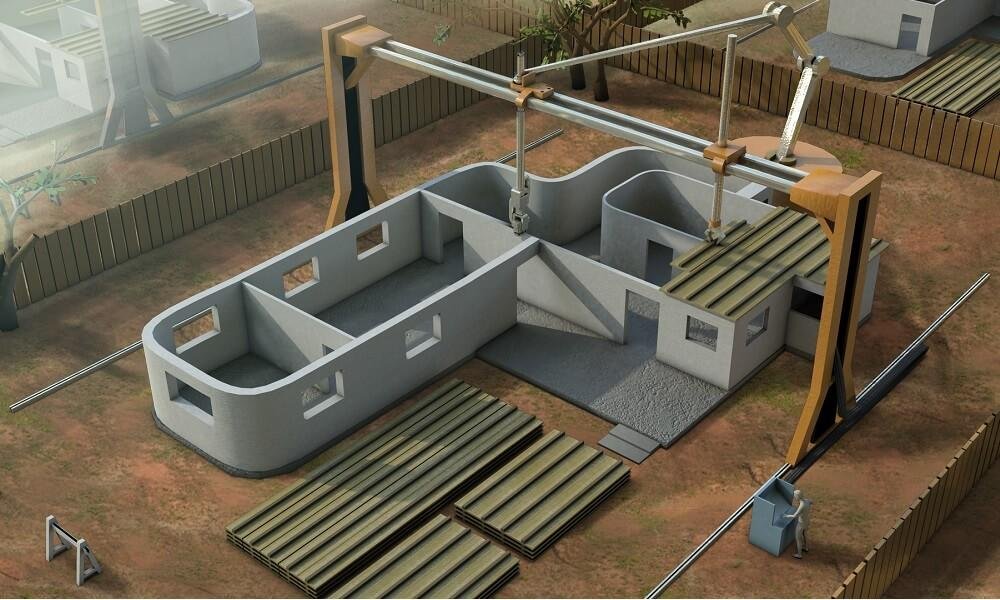
In the realm of architecture, the vivid rise of 3D construction printing is carving curious trajectories within concrete walls and polymer boundaries. This metamorphosis isn’t so much an innovation as it is a swift decline of certain traditional procedures. Although analog builders still employ trowel and rebar, these companies redirect the industry’s cognitive focus to adaptive robotic arms and extruders unexpectedly humming at dawn.
COBOD International
COBOD International shoulders a significant load in this shifting landscape. Headquartered in Denmark, its BOD2 printer—a modular gantry system—offers flexible material handling angles rarely observed in conventional builds. The partnership with material enterprises like Holcim amplifies their capability: delivering not just preset forms but also extraordinary print speeds that decompose old time constraints unexpectedly. Oddly enough, COBOD’s involvement with constructing Europe’s first printed school in Lviv does reinforce the narrative of human-centered innovation despite their mechanical approach.
Apis Cor
A proprietary suite featuring printers named Frank, Gary, and Mary might suggest whimsy; nonetheless Apis Cor demonstrates gravitas by merging robotics with reinforced concrete results comparable—perhaps even superior—to block wall structures. Their commitment to automation swerves construction timelines toward unpredictably efficient outcomes. In subtle contradiction to earlier hesitations about building heights, Apis Cor now advocates low-rise housing design via robot orchestration to curb both demand spikes and lingering errors.
Constructions-3D
Based outside mainstream spotlights yet carrying undeniable heft, Constructions-3D pursues adaptability over mere scale. Their systems support wild swings between intimate bespoke cottages and monumental pavilions: versatility woven straight into machine firmware rather than external accessories.
Mighty Buildings
Not strictly confined by concrete norms or even regulatory frameworks (which seem occasionally perplexed), Mighty Buildings delves into composite materials such as Light Stone Material (LSM). They can produce insulated envelope systems faster than the rhythmical tempo expected from additive manufacturing platforms.
CyBe Construction
From the Netherlands’ inventive workshop corridors emerges CyBe Construction—not solely content with high-speed printing but focusing doggedly on process education for third-party operators worldwide. For them, certification schemes break monotony while fostering collective expertise dissemination during seminars attended by architects unafraid of new jargon or precarious timelines.
SQ4D
Contrary to those assuming American suburbia would hesitate before machinery intervention on building sites—SQ4D proves otherwise via demonstration homes accepted under U.S.-based housing codes. Their Autonomous Robotic Construction Systems sometimes favor quirky lot placements where standard crews typically lose patience halfway through excavation.
XtreeE
XtreeE maintains headquarters near Paris but frequently collaborates globally on digitally crafted latticework components seamlessly integrated into infrastructure projects continuing beside bridges or disused rail lines. For them digital customization means less waste rather than smoother facades—a crucial aspect frequently missed when analysts assess only surface-level aesthetics instead of lifecycle efficiency gains.
WASP (World’s Advanced Saving Project)
Distinguished partly for environmental underpinning as much as open-source principles, WASP develops strategies based around locally sourced materials: clay composites combined unconventionally with straw—or even more outlandish fibers given adequate local abundance. Their Delta WASP machines create large domes wherein ergonomics intersect surprising geometry inflections unlikely replicated through manual craftsmanship alone.
“WASP’s dedication towards sustainable fabrication using what earth already offers sets new dialects for architectural expression each season.”
Despite strong movements toward cement-based approaches previously considered inevitable for structural reliability across wind loads or seismic activity charts—they now pivot back toward ancient earth mixes interlaced through parametric logic seldom forecasted ten years ago.
MudBots 3D Concrete Printing LLC
Overlooking Utah desert expanses sits MudBots—a company disregarding geographical limitations entirely by producing printers that oscillate from compact home kits up to stadium-scale configurations spanning one hundred feet wide at maximum stretch capacity. Hempcrete? Check. Geopolymer? Certainly viable within firm boundaries here too. The company values robust repeatability—their machines might ignore drywall altogether if users prefer monolithic panels denoting both structure and finish simultaneously.
StoneFlower3D
In Moscow’s quieter districts operates StoneFlower3D where granulated mixes pass hydraulic calibration tests before ever flowing down extrusion nozzles primed for precise layering inside insulated jobsite tents—even mid-winter prints proceed without noteworthy delays if mixtures retain specified viscosity curves at subzero temperatures. Odd combinations—sand additives plus kinetic admixtures—surface regularly under their experiments charted less predictably compared to peers further west; a testament perhaps that improvisational engineering remains alive eastward from Berlin domain boundaries despite daunting financial obstacles facing some others listed above who have since folded operations last year after achieving notable success…
Throughout these diverse ventures rumbling across continents—from Katowice workshops up north down into Sicilian ink-stained valleys—the one unifying thread persists: relentless pursuit of construction paradigms untethered from mold-based repetition yet deeply anchored by craft memories unique among all fabricating disciplines known today. And yet some disagree whether this wave represents genuine revolution or simply an oblique angle taken along familiar technological aspirations! Regardless—invisible hands steer poured aggregate alongside fresh algorithmic thinking shaping every structural future mapped out beneath tomorrow’s evolving skylines.